One of the most powerful aspects of new AI tools is the ability to ask it to help with tasks that have seemed out of reach for normal NetSuite users for years.
Yes, I am talking about the dreaded “saved search formulas.”
The ability of AI to search through multiple help guides, code repositories, and internet posts allow if to give users the power to master advanced SQL formulas for saved searches in 10-15 minutes instead of 3 months of videos and research.
In this blog post we will review some of the best ways to leverage AI tools to take your saved searches and dial them to 11.
The Basics
First off, let’s address some of the basics to be aware of when using AI for searches.
AI copilots (e.g., Microsoft Copilot, ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini) are fantastic for ideation and syntax scaffolding—especially when you’re building saved search formulas or SuiteQL queries. They can’t log into NetSuite and create a search, but they can tell you what to do. The following are helpful tips to get you should know before you get started:
- Frame the data problem, not your data.
Describe the entities and relationships (e.g., “Transactions → Lines → Items; need open invoices >30 days, by customer and subsidiary”). Don’t share PII or proprietary values.
- Ask for multiple drafts.
Have the AI propose 2–3 alternative formulas/queries with comments and edgecase tests.
- Translate to NetSuite specifics.
Request Oraclestyle syntax (NetSuite formulas use Oracle SQL functions; SuiteQL is ANSI SQL flavored by Oracle). You can do this by asking it to do what you need “in NetSuite”
- Validate in a sandbox.
Paste the idea into your saved search or SuiteQL runner; fix any field IDs, joins, or date functions. Testing in sandbox is always wise, though saved searches don’t carry as much risk if you are not using them in scripts or to manipulate other data.
- Harden & document.
Have the AI generate inline comments, test data assumptions, and failure modes.
Governance tip: Keep AI prompts metadataonly (table names, field IDs, desired logic). Never paste customer names, invoice numbers, addresses, or confidential prices into thirdparty tools. Always follow your company’s internal IT and PII policies when exploring using AI.
Prompt patterns you can copy/paste
Learning HOW to ask an AI tool a question is just as important to getting good answers as all the coding and work that goes into the tools.
The more specific the request is, the better the answer will be.
Here are four prompt examples and examples of what an AI might produce:
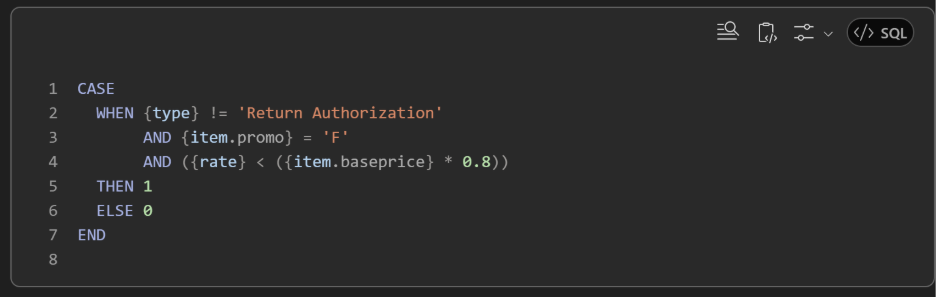
1) Marginleak detector (linelevel)
“Draft a formula (numeric) for a Transaction Line search that flags lines where effective discount exceeds 20% vs. item base price, excluding promo items and returns. Include comments.”
Example of results:
2) Saved Search formula (A/R aging buckets)
“I’m creating a NetSuite Transaction saved search for invoices. Draft a formula (numeric) that returns 1 if the invoice is 31–60 days overdue relative to today, else 0. Use Oraclestyle functions you’d expect in NetSuite formulas. Also provide a humanreadable formula (text) label.”
Example of the results:
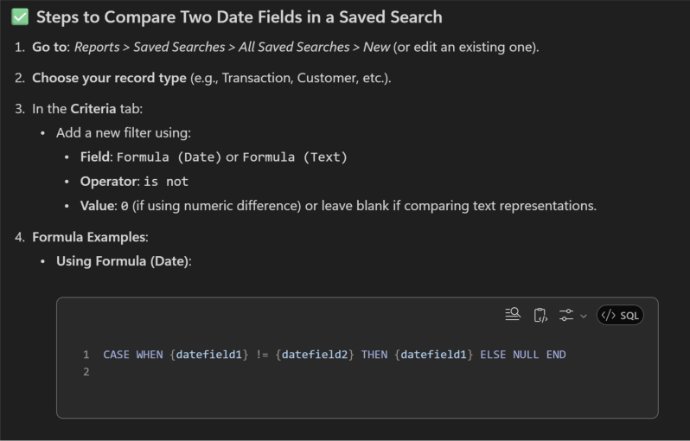
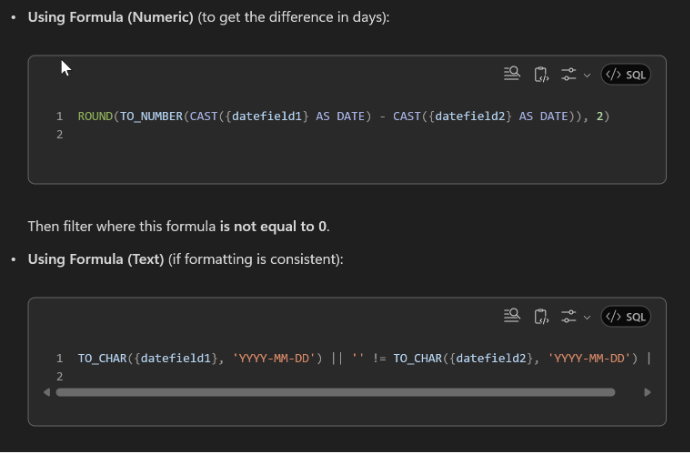
3) “Comparing Dates”
“How do I a write a saved search in NetSuite that returns results if two date fields don’t match”
Example Response:
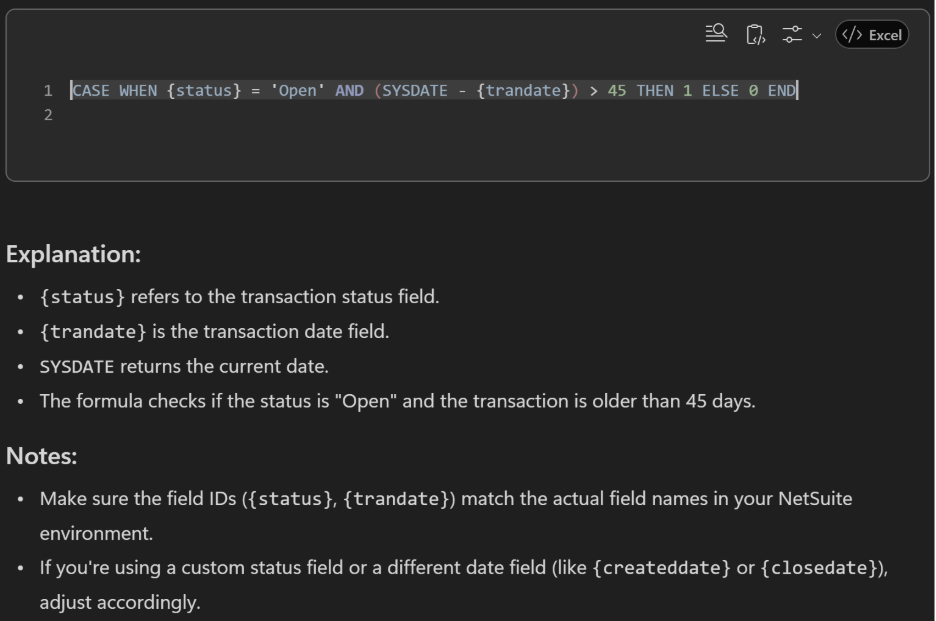
4) “Translate Excel logic to NetSuite formula”
“Convert this Excel logic (IF(AND(A2=’Open’,TODAY()-D2>45),1,0)) into a NetSuite formula (numeric) that works in a Transaction saved search.”